Since 1991, Ocean Warming 60% Faster Than Estimated; Argo Float Network Made Study Possible
EDIT
The new study finds that since 1991, the oceans have warmed about 60 percent faster than the average rate of warming estimated by studies summarized by the IPCC, which are based on data from Argo floats. This is a big deal. Most of the difference comes from the earliest part of this period, before there were enough Argo floats in the oceans to properly represent the three-dimensional distribution of global water temperatures. The new data are complete all the way back to 1991, but the Argo data were really sparse until the mid-2000s.
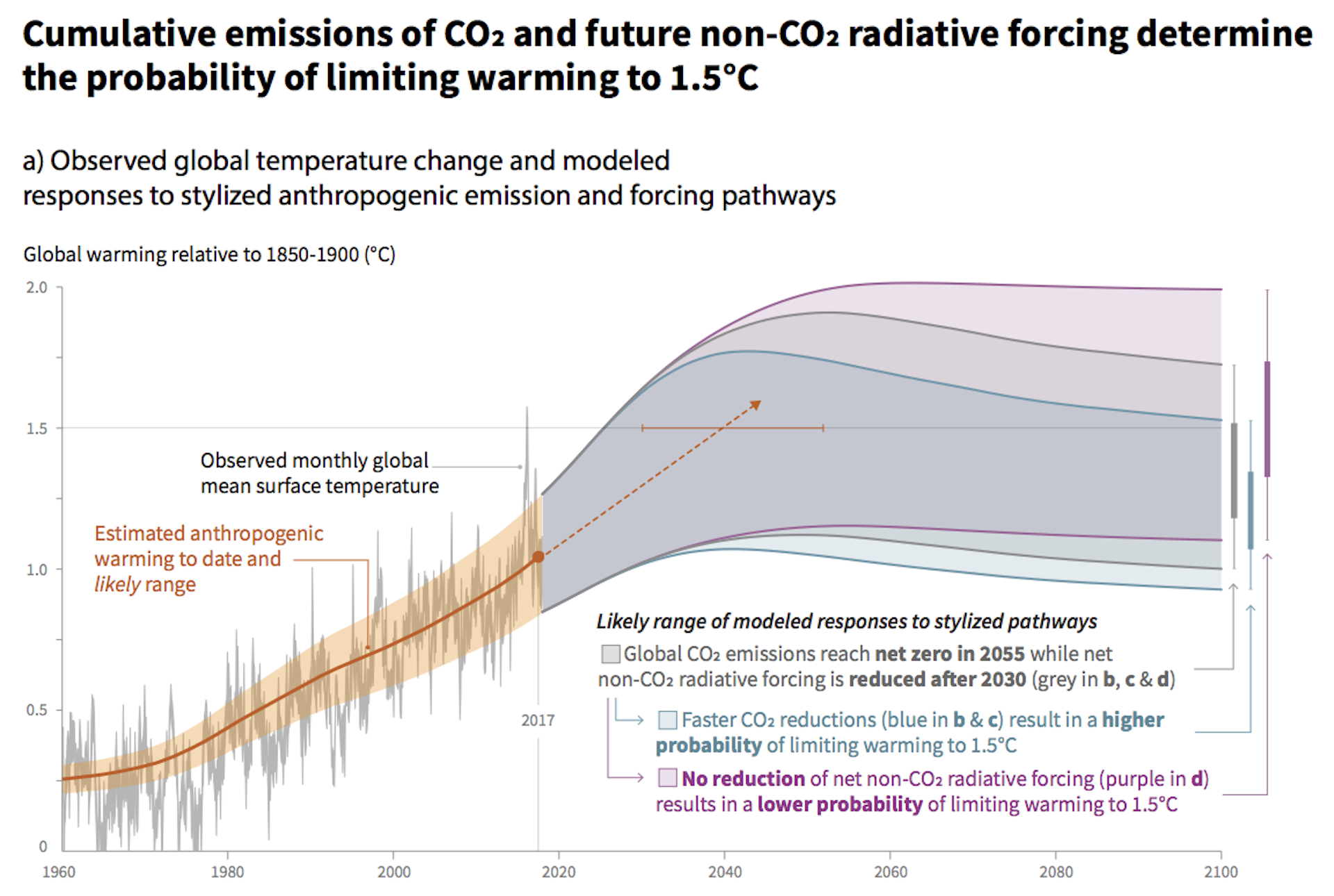
The implication of faster ocean warming is that the effect of carbon dioxide on global warming is greater than we’d thought. We already knew that adding CO2 to the air was warming the world very rapidly. And the IPCC just warned in a special report that limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels – a target that would avert many extreme impacts on humans and ecosystems – would require quickly reducing and eventually eliminating coal, oil and gas from the world energy supply. This study doesn’t change any of that, but it means we will need to eliminate fossil fuels even faster.
 ?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&q=45&auto=format&w=754&fit=clip
?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&q=45&auto=format&w=754&fit=clip
To limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, the IPCC warns that greenhouse gas emissions would need to be drastically reduced over approximately the next decade. Credit: IPCC, CC BY-ND
(Researchers) have measured tiny changes since 1991 in the concentrations of a few gases in the air – oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide – with incredibly high precision. This is really hard to do, because the changes are extremely small compared to the large amounts already in the air. Some of these gases from the air dissolve into the oceans. The water’s temperature dictates how much it can absorb. As water warms, the amount of a gas that can dissolve in it decreases – that’s why a soda or beer left open on the kitchen table goes flat. That same temperature dependence allowed the scientists to calculate total changes in global ocean heat content from 1991 to now, just using very precise measurements of the air itself.
EDIT
This study very cleverly used data from the composition of the air itself going back nearly 30 years. We didn’t have Argo floats back then, but air samples are still available that can be analyzed decades later. Using a longer record of warming is much better for estimating the rate, because it’s less sensitive to year-to-year variations than a shorter record.
EDIT
https://www.desmogblog.com/2018/11/06/new-findings-faster-ocean-warming-climate-change
 ?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&q=45&auto=format&w=754&fit=clip
?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&q=45&auto=format&w=754&fit=clip