Arctic Sea Ice Mean Extent By Decade - This Year's Maximum Mirrors May Averages Durng 1980s
EDIT
As winter turns into spring in the northern hemisphere, Arctic sea ice stops growing and reaches its peak extent for the year. This marks the end of the half-year ice growth season that started with the sea ice minimum – the sixth lowest on record – in September last year.
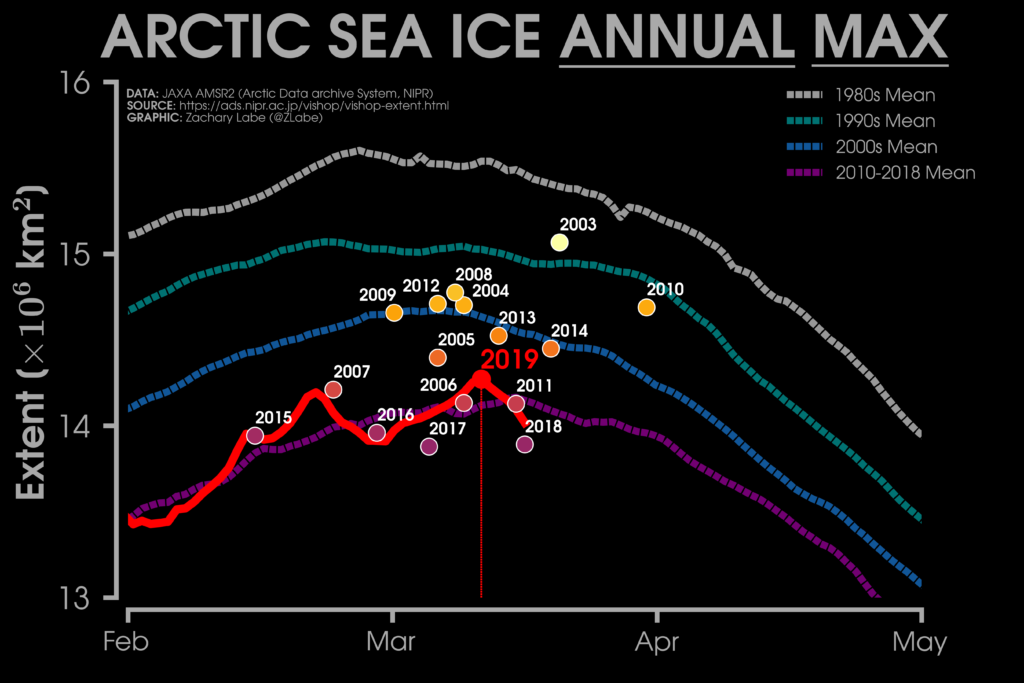
Scientists use satellites to monitor sea ice extent, recording the size and date of the annual maximum when it peaks each year. Along with the summer minimum, it is one of the key metrics for tracking the “health” of the Arctic’s sea ice. The winter peak extent for 2019 is estimated at 14.78m sq km, the NSIDC says. It was recorded on the 13 March – just one day out from the median winter maximum date of 12 March in the 1981-2010 average.
It sits alongside 2007 as the seventh smallest winter peak on record, says the NSIDC. The four smallest in the satellite era occurred between 2015 and 2018. The map below shows Arctic sea ice on the day of this year’s peak. The orange line shows the average position on that day for the long-term average.
EDIT
That sea ice in the Barents Sea is back to near-average conditions this year is “especially interesting”, says Prof Julienne Stroeve, a professor of polar observation and modelling at University College London and senior research scientist at the NSIDC. In recent years “the ice edge was much further north”, she tells Carbon Brief. Low sea ice cover has been linked to the “Atlanticification” of this sea as it shifts from being dominated by cold, fresh Arctic waters to a warm, salty Atlantic regime. The declining condition of winter sea ice over the past four decades has a knock-on effect in the summer too, says Dr Ron Kwok, a senior research scientist at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology. He tells Carbon Brief:
“The replacement of large fractions of the Arctic Ocean with seasonal ice is a large factor in this behaviour [the high year-to-year variability] – the ‘new normal’ – because the seasonal ice grows faster but not enough to survive the summer.”
EDIT
https://www.carbonbrief.org/arctic-sea-ice-winter-peak-in-2019-is-seventh-lowest-on-record
