The second version of the Klan was not just directed against African-Americans, but against the changing demographic in the US due to immigration, about 100 years ago. The Tea Party is really all about fears of a changing America that is getting less white every day.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ku_Klux_Klan
In 1915, the second Klan was founded in Atlanta, Georgia. Starting in 1921, it adopted a modern business system of recruiting (which paid most of the initiation fee and costume charges as commissions to the organizers) and grew rapidly nationwide at a time of prosperity. Reflecting the social tensions of urban industrialization and vastly increased immigration, its membership grew most rapidly in cities, and spread out of the South to the Midwest and West. The second KKK preached "One Hundred Percent Americanism" and demanded the purification of politics, calling for strict morality and better enforcement of prohibition. Its official rhetoric focused on the threat of the Catholic Church, using anti-Catholicism and nativism.[4] Its appeal was directed exclusively at white Protestants.[20] Some local groups took part in attacks on private houses and carried out other violent activities. The violent episodes were generally in the South.[21]
The second Klan was a formal fraternal organization, with a national and state structure. At its peak in the mid-1920s, the organization claimed to include about 15% of the nation's eligible population, approximately 4–5 million men. Internal divisions, criminal behavior by leaders, and external opposition brought about a collapse in membership, which had dropped to about 30,000 by 1930. It finally faded away in the 1940s.
and another history
http://www.history.com/topics/ku-klux-klan
In 1915, white Protestant nativists organized a revival of the Ku Klux Klan near Atlanta, Georgia, inspired by their romantic view of the Old South as well as Thomas Dixon's 1905 book "The Clansman" and D.W. Griffith's 1915 film "Birth of a Nation." This second generation of the Klan was not only anti-black but also took a stand against Roman Catholics, Jews, foreigners and organized labor. It was fueled by growing hostility to the surge in immigration that America experienced in the early 20th century along with fears of communist revolution akin to the Bolshevik triumph in Russia in 1917. The organization took as its symbol a burning cross and held rallies, parades and marches around the country. At its peak in the 1920s, Klan membership exceeded 4 million people nationwide.
The Great Depression in the 1930s depleted the Klan's membership ranks, and the organization temporarily disbanded in 1944. The civil rights movement of the 1960s saw a surge of local Klan activity across the South, including the bombings, beatings and shootings of black and white activists. These actions, carried out in secret but apparently the work of local Klansmen, outraged the nation and helped win support for the civil rights cause. In 1965, President Lyndon Johnson delivered a speech publicly condemning the Klan and announcing the arrest of four Klansmen in connection with the murder of a white female civil rights worker in Alabama. The cases of Klan-related violence became more isolated in the decades to come, though fragmented groups became aligned with neo-Nazi or other right-wing extremist organizations from the 1970s onward. In the early 1990s, the Klan was estimated to have between 6,000 and 10,000 active members, mostly in the Deep South.
Klan march at the peak of popularity in 1925 in our nation's capital.


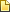 = new reply since forum marked as read
= new reply since forum marked as read

